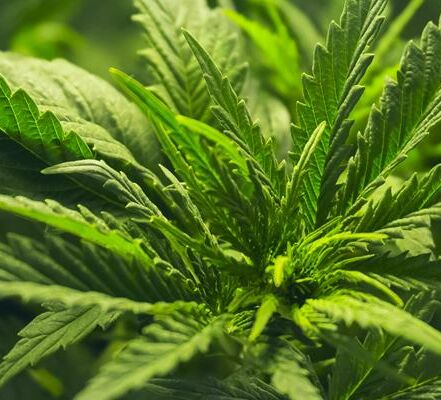
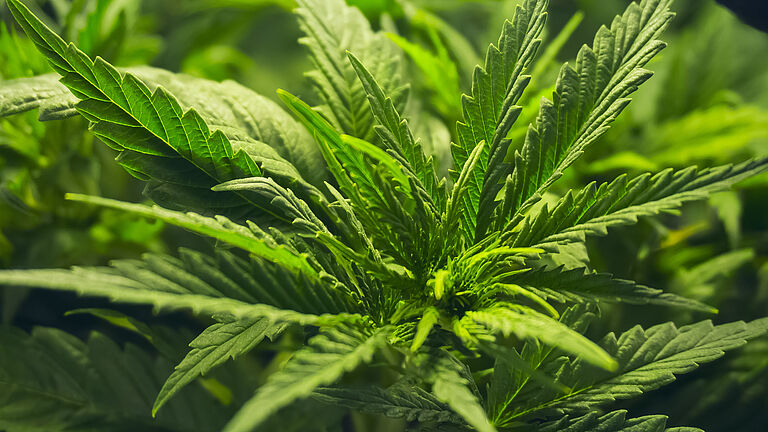
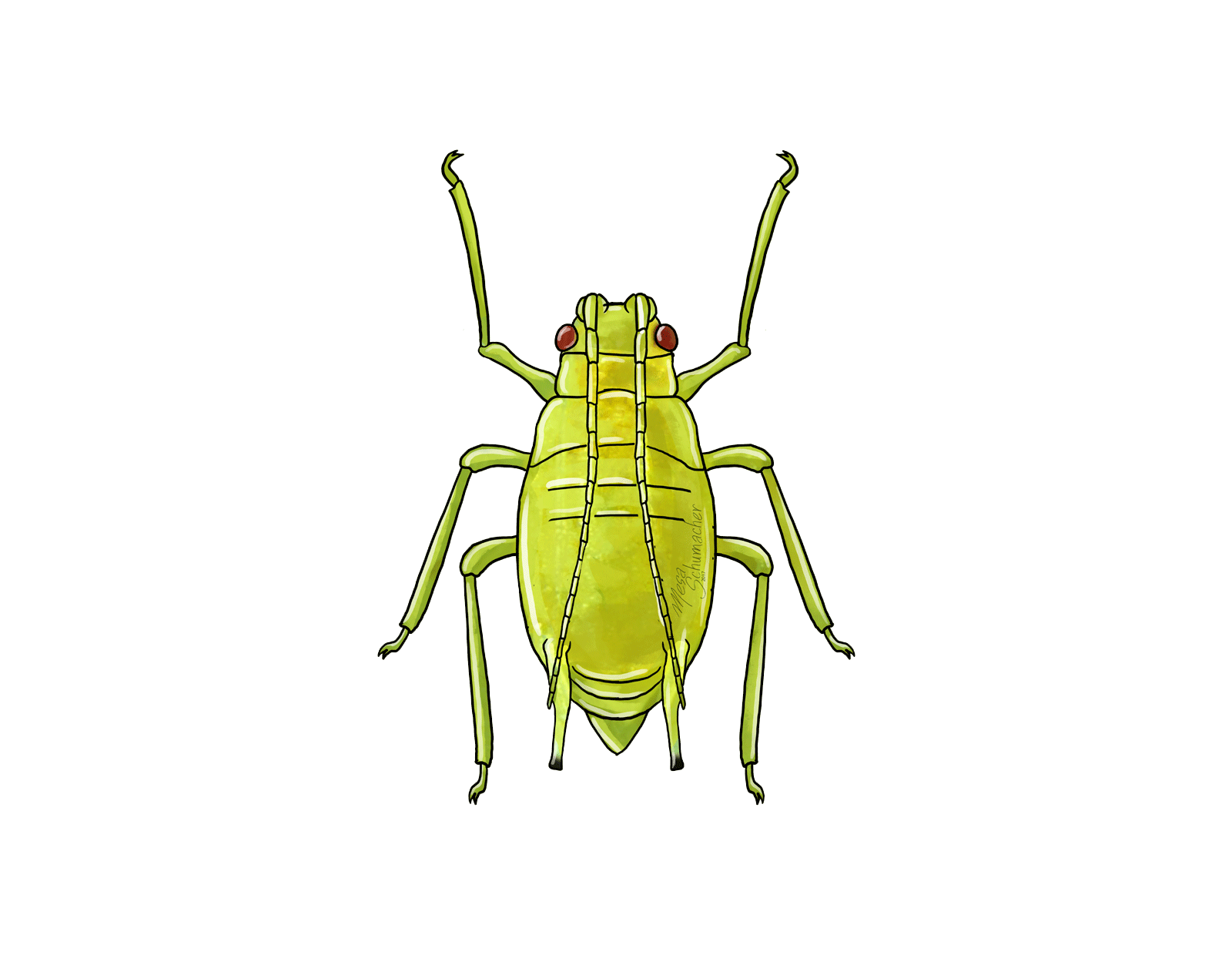
Aphids
Aphids pose a significant challenge in cannabis cultivation, with several prominent species specifically affecting the crop. Notably, the Cotton aphid (Aphis gossypii), the Potato aphid (Macrosiphum euphorbiae), the Green peach aphid (Myzus persicae), the Cannabis aphid (Phorodon cannabis), and the Rice root aphid (Rhopalosiphum rufiabdominale) are among the key aphid species that can infest cannabis plants. These pests have the potential to cause substantial damage as they feed on the plant's sap and reproduce rapidly. Their feeding activities can lead to stunted growth, distorted leaves, and even the transmission of viral diseases.
Leaf miners
Leaf miners are a challenge to cannabis crops, and several species stand out as significant pests. Tomato leaf miner (Liriomyza bryoniae), Pea leaf miner (Liriomyza huidobrensis), and American serpentine leaf miner (Liriomyza trifolii) are among the most notorious leaf miner species affecting cannabis. These tiny insects lay their eggs in cannabis leaves, and the larvae that hatch proceed to tunnel through the leaf tissue, creating distinctive winding mines that can severely damage the foliage. As a result, the plant's ability to photosynthesize and produce energy is compromised, leading to reduced yields and overall weakened cannabis plants.
Mealybugs
In some cases, mealybugs can be a problem in cannabis. These small, soft-bodied insects feed on the sap of cannabis plants, causing stunted growth and yellowing of the leaves. Their waxy, cotton-like appearance makes them easily recognizable on the plant surfaces. Mealybug infestations can weaken cannabis plants and impact overall yields.
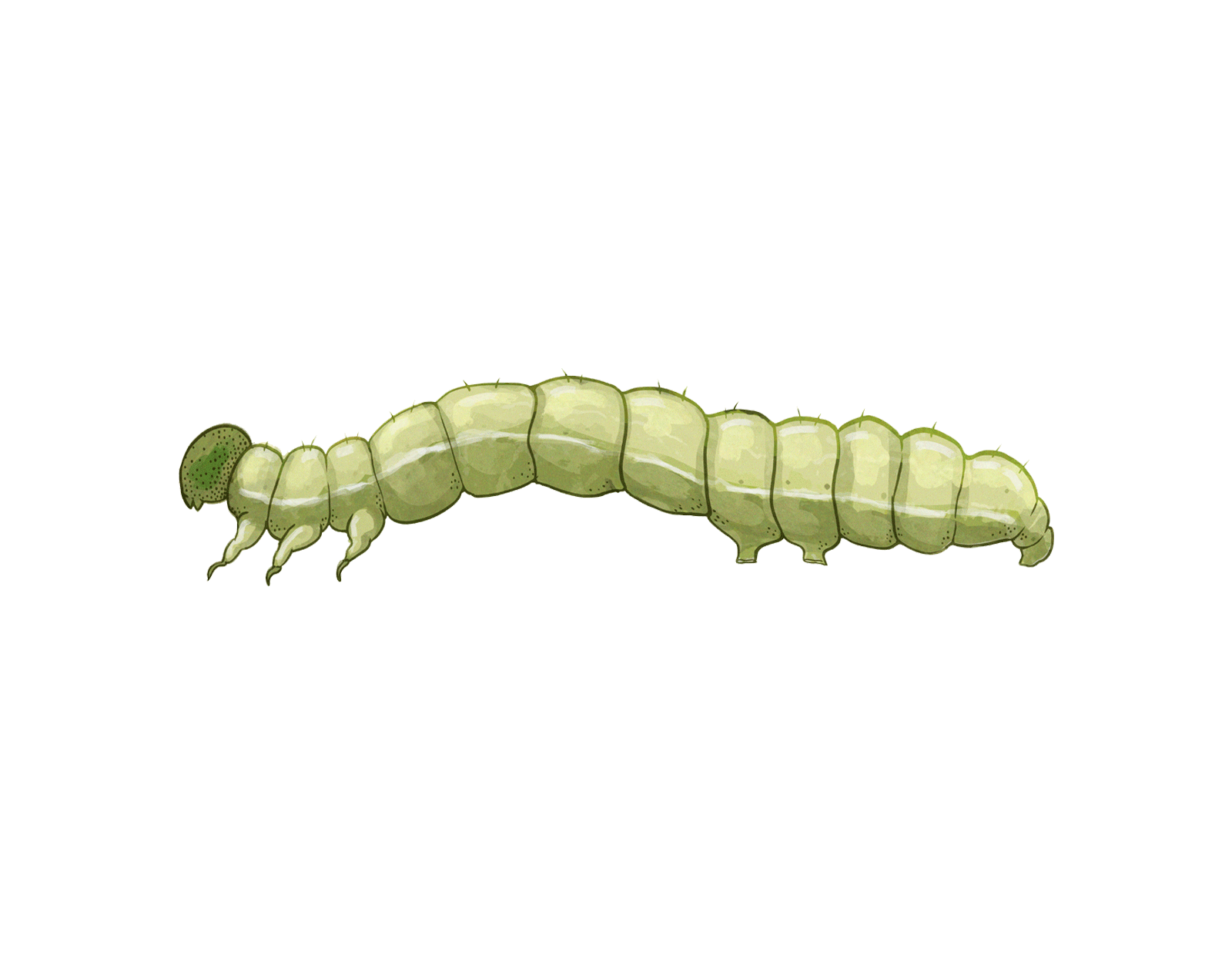
Caterpillars
Caterpillars can present significant challenges to cannabis cultivation, with various species wreaking havoc on the plants. Two particularly notorious pests are the Hemp moth (Grapholita delineana) and the Beet armyworm (Spodoptera exigua). The presence of Grapholita delineana caterpillars often leads to the manifestation of bud rot and decreased yield as they tunnel into developing flower buds, leaving them susceptible to fungal infections. On the other hand, the voracious appetite of the Spodoptera poses a threat as they defoliate cannabis plants, weakening their overall health and vitality.
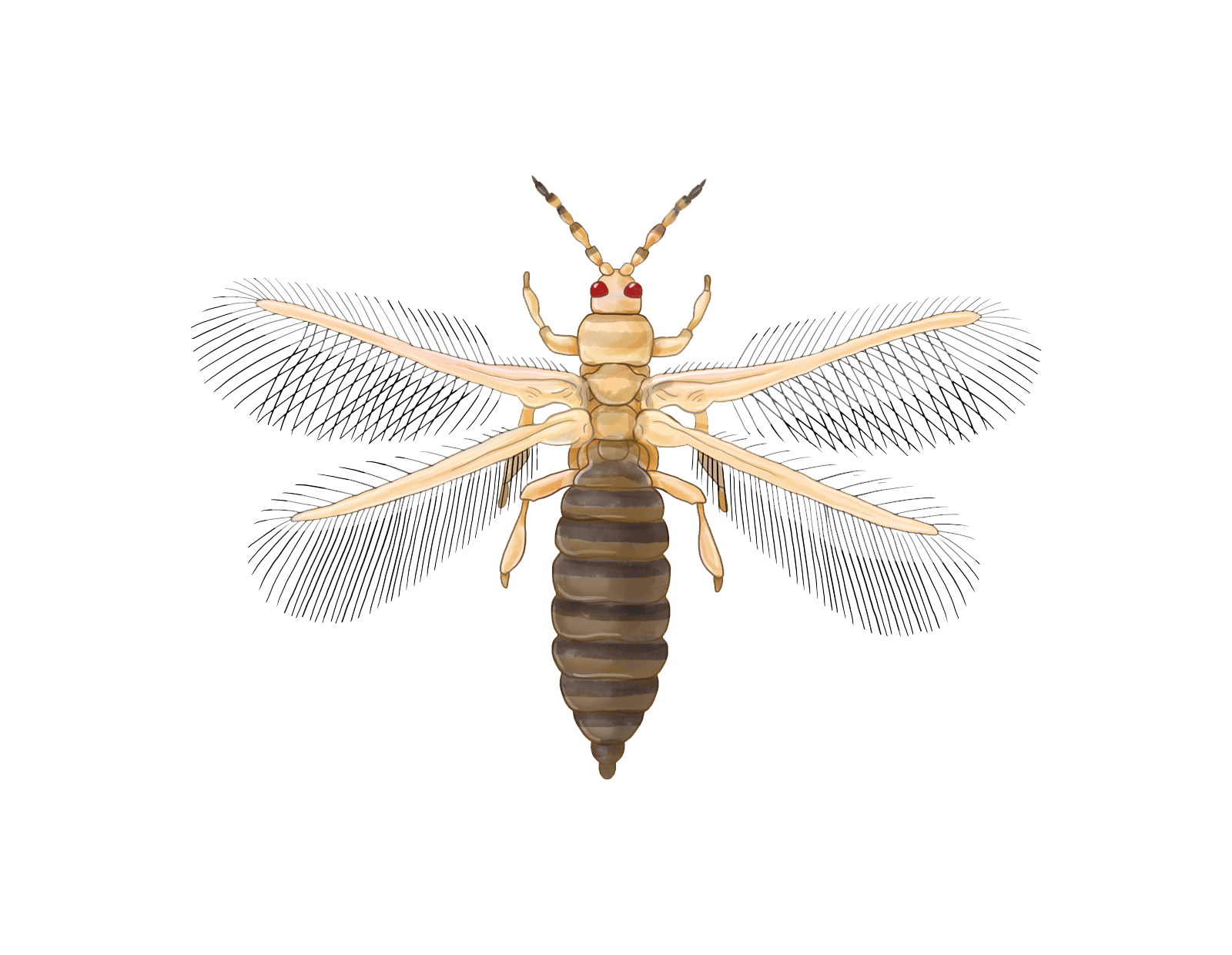
Thrips
Thrips pose a persistent threat to cannabis crops, with species like Western flower thrips (Frankliniella occidentalis), Onion thrips (Thrips tabaci), and Impatiens thrips (Echinothrips americanus) causing notable concern. These tiny insects have the potential to inflict substantial damage by puncturing plant cells and feeding on the sap, ultimately stunting growth and causing deformities in leaves and flowers.
Whitefly
Whitefly can be highly problematic in cannabis, with two notable species of concern being the Tobacco whitefly (Bemisia tabaci) and Greenhouse whitefly (Trialeurodes vaporariorum). These small, winged insects feed on cannabis plants by piercing the phloem and extracting sap, leading to yellowing, wilting, and reduced plant vigor. Whitefly infestations can cause significant damage, hinder plant growth, and ultimately impact yields. Furthermore, whiteflies are known to secrete honeydew, promoting the growth of sooty mold that further interferes with photosynthesis.
Plant bugs
Lygus spp. pierce through plant tissues and feeds on the sap, causing distorted growth and blemished leaves in cannabis crops. Furthermore, its feeding behavior can lead to the development of necrotic spots and reduced flower quality.
Spider mites
Tetranychus urticae, also known as the Two-spotted spider mite, inflicts considerable harm to cannabis crops by piercing plant cells and extracting essential fluids, resulting in stippled leaves, webbing, and a general decline in plant health. These mites are notorious for their rapid reproductive rates, enabling them to swiftly multiply and overrun cannabis crops.
Other pest mites
Russet mites, such as the Hemp russet mite (Aculops cannabicola) are troublesome pests within the Eriophyidae family, which have a notable impact on cannabis plants. Aculops cannabicola infests cannabis crops, leading to distorted growth, necrosis, and decreased yields. The Broad mite (Polyphagotarsonemus latus) is a mite of the family Tarsonemidae and can also be a severe problem in cannabis crops.
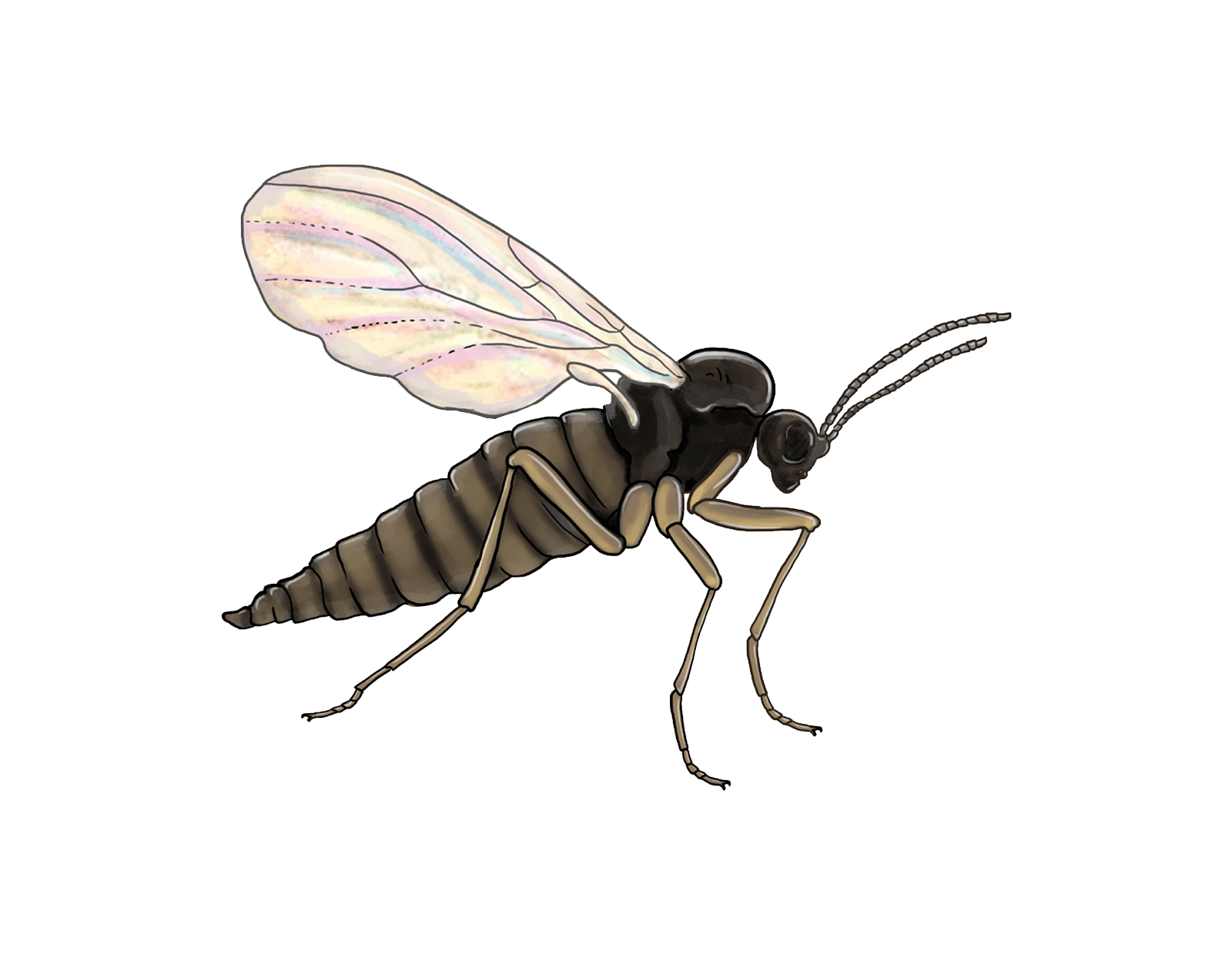
Fungus gnats
Fungus gnats or Sciarid flies can wreak havoc on cannabis plants, particularly in indoor growing environments. Fungus gnats like Bradysia impatiens are small flies that lay their eggs in damp soil. Their larvae feed on organic matter in the soil and can damage the roots of cannabis plants, leading to stunted growth and decreased vigor. The presence of these pests can also increase the risk of fungal diseases. Sciaridae species share similar habits and can contribute to the overall stress and reduced health of cannabis plants.